Get Our Latest Updates
Alpro Group Head Office & Distribution Centre
Unit V1-A, Lot 45880, Jalan Techvalley 3/2, Sendayan Techvalley, 71950 Bandar Sri Sendayan, Negeri Sembilan.
family-doctor

Key Points:
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition with high blood sugar, where early detection prevents complications and improves quality of life.
Risk factors include obesity, family history, inactivity, and chronic conditions, making regular screening essential.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic health conditions that affects millions of people on a global scale. It poses significant risks to both individual health and public health systems. Early detection of diabetes mellitus is not just beneficial; it is transformative. It allows for prompt intervention and effective disease management, preventing complications and enhancing overall quality of life. Here, we will explore why it is crucial to identify diabetes early and how this can make a profound difference in health outcomes.
Diabetes mellitus involves high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) due to poor glucose use or excess consumption of high-carb foods. Glucose metabolism disorders include impaired fasting glucose (IFG), impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), and overt diabetes.
In Malaysia, 90% of cases are Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), linked to obesity, inactivity, family history, and pregnancy-related diabetes. Similar trends are seen worldwide, driven by modern lifestyles and urbanization.
T2DM is associated with abdominal fat, insulin resistance, and declining pancreatic function. It mainly affects adults, while Type 1 Diabetes (T1DM), an autoimmune condition, is more common in children. This article focuses on T2DM detection and screening.

Early stages of mild diabetes are often asymptomatic, and mild hyperglycemia may progress undiagnosed until classical symptoms start to appear. It is important to detect diabetes early and to initiate management promptly to prevent complications(4).
Common Early Signs of Diabetes:
Signs of Insulin Resistance:
How Skin Patches Can Indicate Diabetes:
Dark, velvety patches known as acanthosis nigricans often appear on the neck, underarms, or other skin folds. These patches can signal insulin resistance, a key risk factor for T2DM. Noticing these skin changes on yourself or a loved one may prompt a timely discussion with a healthcare provider. In fact, family and friends play a vital role in encouraging one another to get screened.
Untreated diabetes can lead to several health issues, mainly vascular complications:
These complications are caused by:
Comorbidities like high blood pressure and high cholesterol can worsen these problems.
Microvascular diseases can result in severe complications, such as:
Common macrovascular complications include heart attacks and strokes, which greatly affect overall health.
High blood sugar can also lead to immune dysfunction, making infections more likely.
Early detection of diabetes can help limit damage, reduce the burden of disease, and encourage healthier lifestyles.
In Malaysia, most healthcare personnel are well-versed in managing diabetes and its complications. There is no specific age limit for starting diabetes screening, as even adolescents or young adults at risk may develop diabetes mellitus.
If early signs of diabetes appear, screening should be done before confirmatory tests. Many patients are asymptomatic, but factors like BMI, waist circumference, heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, endocrine disorders, and chronic medication use can prompt screening.
Screening Criteria as per Malaysian Guidelines
1. Symptomatic individuals
2. Women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)
3. Adults with risk factors (overweight/obese with BMI >23 or increased waist circumference: ≥80 cm for females, ≥90 cm for males) and any of the following conditions:
4. Prediabetics
5. Adolescents
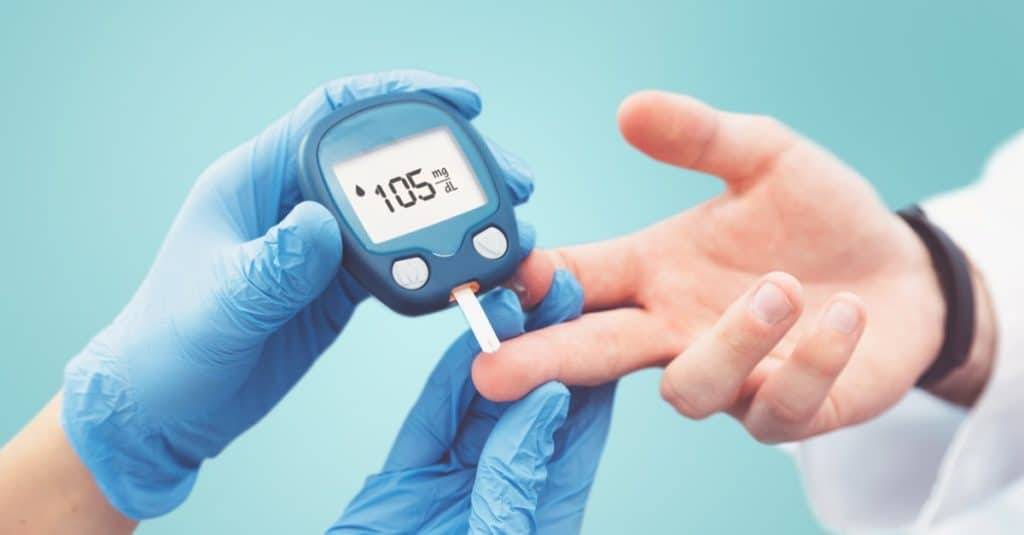
Screening is usually done via a pinprick test, which is a simple office test. Readings that exceed 5.6 mmol/L for fasting or 7.8 mmol/L for random samples should be referred for confirmatory tests. Although the presence of sugar in urine may also be used to detect early signs of diabetes, contamination or improper collection methods can compromise test results. Therefore, the pinprick test offers better consistency as a diabetes screening method.
Confirmatory tests should be conducted at healthcare facilities under the supervision of qualified healthcare personnel. Diabetes can be confirmed with a fasting blood sugar level, HbA1c level, or through an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT).
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Random Blood Sugar Levels
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
HbA1c Test
While readings above 6.3% generally indicate diabetes mellitus, it is inappropriate to use as a diagnostic test in certain conditions affecting hemoglobin levels, such as anemia, pancreatic disorders, chronic kidney diseases, or in adolescents/teenagers.
Public health initiatives that raise awareness about the risk factors and symptoms of diabetes are essential. Education encourages individuals to seek screening and monitor their health, while community programs and online resources empower them to take charge of their well-being. Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly improve outcomes and reduce complications.
Early detection plays a crucial role in ensuring better long-term health and quality of life. If you have any questions, consult trusted healthcare personnel, as prevention is always better than cure.
This year, Alpro Pharmacy is offering an RM1 screening throughout November 2024 at all outlets across malaysia. This is a convenient and affordable way to get screened, particularly for those who may be asymptomatic.
Not sure if you’re at risk? Visit your nearest Alpro Pharmacy outlet today for a RM1 blood glucose check.

Consult our healthcare professionals on Alpro E-Pharmacy if you have any health-related concerns. Alpro E-Pharmacy is specially designed to bring convenience to everyone including those who wish to get 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗶𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗮𝗿𝘆 𝗣𝗵𝗮𝗿𝗺𝗮𝗰𝗶𝘀𝘁 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝘂𝗹𝘁𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 or 𝗦𝗮𝗺𝗲 𝗗𝗮𝘆 𝗠𝗲𝗱𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗗𝗲𝗹𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 without stepping out from their comfortable home or even hotel. You can even send medications to your loved ones without hassle! Our pharmacists are always ready to assist.
If you need any further help, you are always welcome to use Alpro E-Pharmacy service on Whatsapp or call our hotline 019-7021923
Disclaimer: No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your qualified health professional.
Get Our Latest Updates
Alpro Group Head Office & Distribution Centre
Unit V1-A, Lot 45880, Jalan Techvalley 3/2, Sendayan Techvalley, 71950 Bandar Sri Sendayan, Negeri Sembilan.
Alpro Alliance Sdn. Bhd. (1015456-V)